Over the years, car audio speakers have been installed in seemingly endless combinations of panels, pods and baffles. Some look great, some sound great and some offer both. Sadly, not everyone understands the physics involved in choosing the ideal installation locations for speakers. This article will cover a few of the vital installation criteria that need to be considered when your local retailer is installing new speakers in your car or truck.
Over the years, car audio speakers have been installed in seemingly endless combinations of panels, pods and baffles. Some look great, some sound great and some offer both. Sadly, not everyone understands the physics involved in choosing the ideal installation locations for speakers. This article will cover a few of the vital installation criteria that need to be considered when your local retailer is installing new speakers in your car or truck.
Every Speaker Needs an Enclosure
If a speaker were set on a table and music played through it, you’d find it doesn’t produce any bass and very little midbass. This is because there’s a nearly equal amount of sound produced from the back of the woofer cone compared to the front. If you wrap your hands around the speaker, the performance improves. If you mount the speaker in a baffle that separates the two sound sources (front and rear), you’ve eliminated back-wave cancellation.
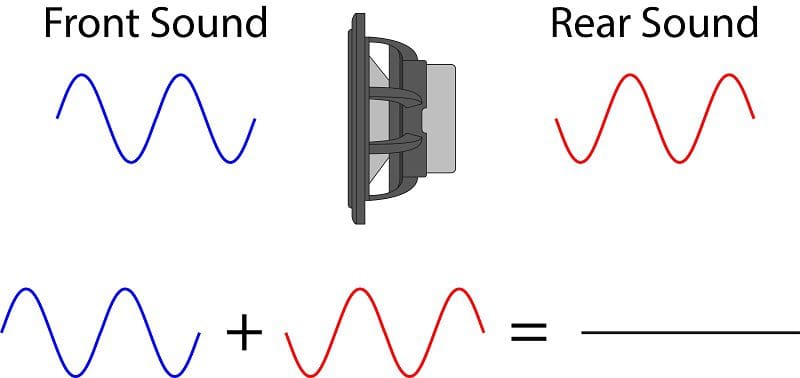
Bass and midrange sound produced by the speaker’s front and rear will cancel each other if the driver is not installed in a proper baffle.
Dash and Door Panel Installations
Of course, one of the most popular locations to mount a speaker is in the factory location in the dash or door of your car or truck in place of the speaker that came from the factory. This location typically provides excellent cosmetics as the vehicle retains its factory-like appearance. In many cases, such as a dash location at the base of the windshield, the speaker’s performance can be such that it delivers excellent frequency response throughout the entire listening environment.
Door Speaker Installation and Sound Deadening
If you have a speaker installed in a door location, your retailer may need to create a set of mounting adapters. A few factors need careful consideration during the design of these adapters. First, they need to be thick enough to ensure that the magnet assembly on the speaker’s rear won’t interfere with the window mechanism or glass. Second, the speaker’s front needs adequate clearance to ensure that the woofer cone can’t come into contact with the grille. Finally, the adapter needs to be made from a material that won’t be damaged by moisture. Most people would be surprised by how much water gets into the door when it rains or when a vehicle goes through a car wash. Common materials for speaker adapters include ABS and expanded PVC plastics. Wood is not a suitable material for use in the doors.
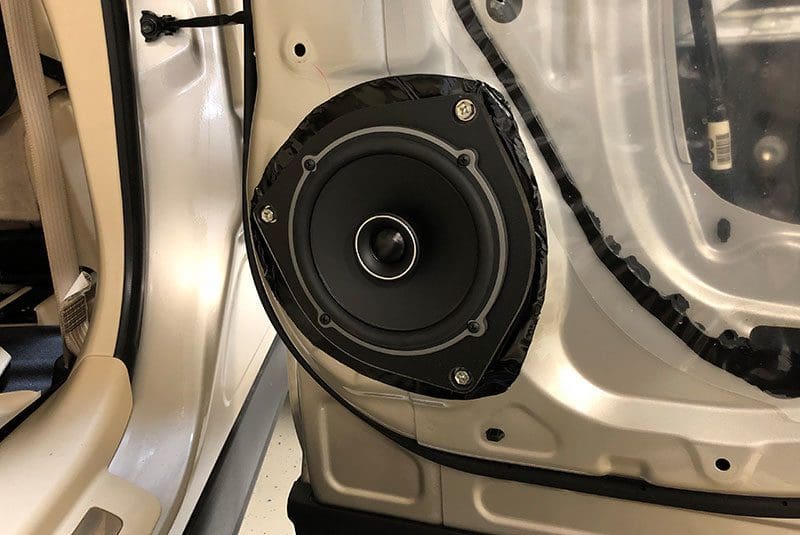

Extreme Audio near Richmond, Virginia, created a set of mounting adapters out of expanded PVC plastic to install new speakers in the rear doors of this 2014 Lexus RX350. They applied a layer of sound deadening to the door to serve as a gasket for the adapter.
Most modern vehicles have openings built into the interior skin of the doors. These openings allow technicians to service the door handles and window mechanism. Unfortunately, these openings also allow the sound from the speaker’s rear to mix with the sound from the front. The easiest way to improve the performance of a speaker mounted in a door like this is to add a layer of sound deadening. The dense butyl material and foam will seal the openings and dramatically improve your speakers’ efficiency and sound quality.
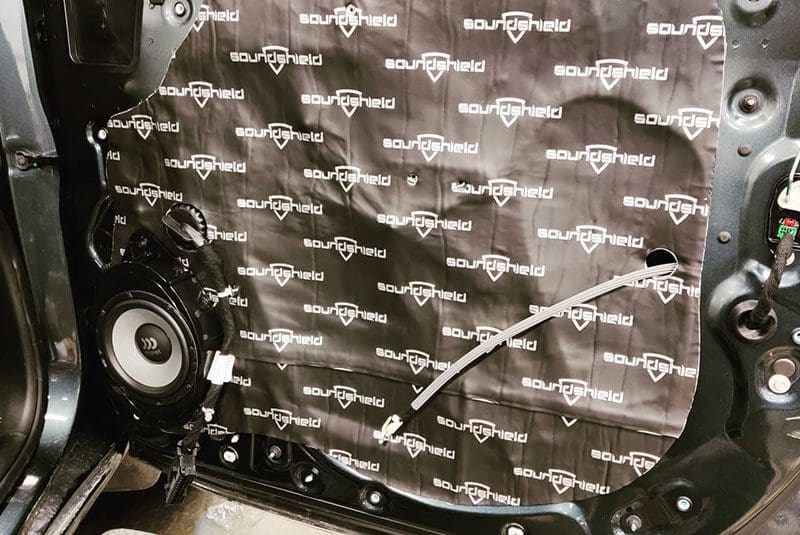

Perfectionist Auto Sound and Security in Anchorage, Alaska, treated the doors of this GMC 2500HD with a layer of SoundShield sound deadening material before installing new Morel speakers.
A Look at Speaker Pods and Enclosures
A common error we see in custom A-pillars and speaker pods is the use of an enclosure that’s too small for the chosen speaker. Even a 4-inch midrange that will play down to 125 Hz needs a certain volume of air in the space behind the driver so as not to affect the overall compliance of the system. If a speaker pod is too small, the system’s resonant frequency will increase and, beyond a certain point, so will the distortion added to the signal. Let’s look at a few examples. It’s quite common to see 6.5-inch coaxial speakers mounted in small enclosures in an amp rack or subwoofer enclosure. Let’s look at a speaker like the BLAM Live-Series LW 165 C 6.5-inch coaxial speaker. Based on the manufacturer’s Thiele/Small parameters, the small sealed enclosure that would be acceptable for this driver would have an internal volume of about 0.3 cubic feet. This enclosure yields a system Q (Qts) of 0.707 and a-3 dB frequency of about 90 Hz.
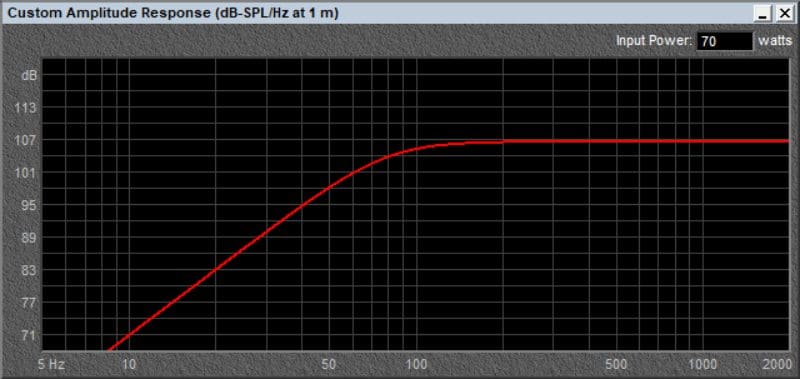
Predicted low-frequency response of a single BLAM LW 165 C 6.5-inch speaker in a 0.3-cubic-foot enclosure.
Where we get into trouble is when an enclosure isn’t large enough. We recently saw a post where a fabricator crammed a driver similar to this into a pod that “was just big enough to house the speaker.” Let’s make this an extreme example and say the interior dimension was 5.5 by 5.5 inches with a depth of 2.5 inches. That’s a mere 0.017 cubic feet.
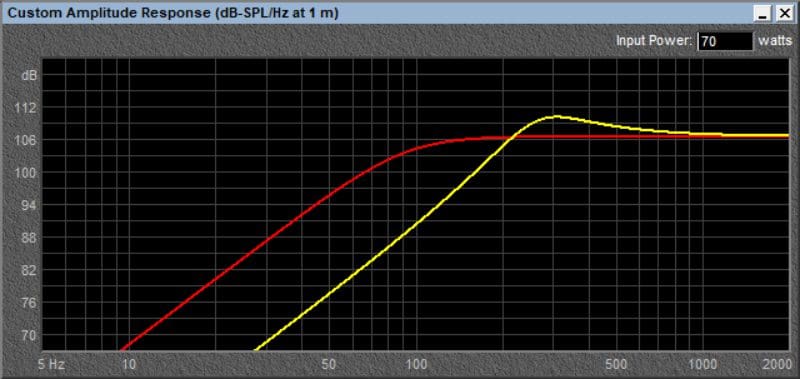
Here’s our 6.5-inch speaker now crammed into a tiny enclosure. There’s an almost 4 dB peak at 305 Hz, and the -3 dB point is now close to 190 Hz. The total system Q has a completely unacceptable value of just over 1.4. Not only would this sound terrible, but it would also be nearly impossible to blend into a subwoofer. Sadly, it happens all the time in cars and trucks and even more often in displays.
To prevent this, every speaker larger than about 2.5 inches in diameter should be modeled using enclosure simulation software to ensure that the planned enclosure won’t be detrimental to the system’s overall performance.
System Directivity
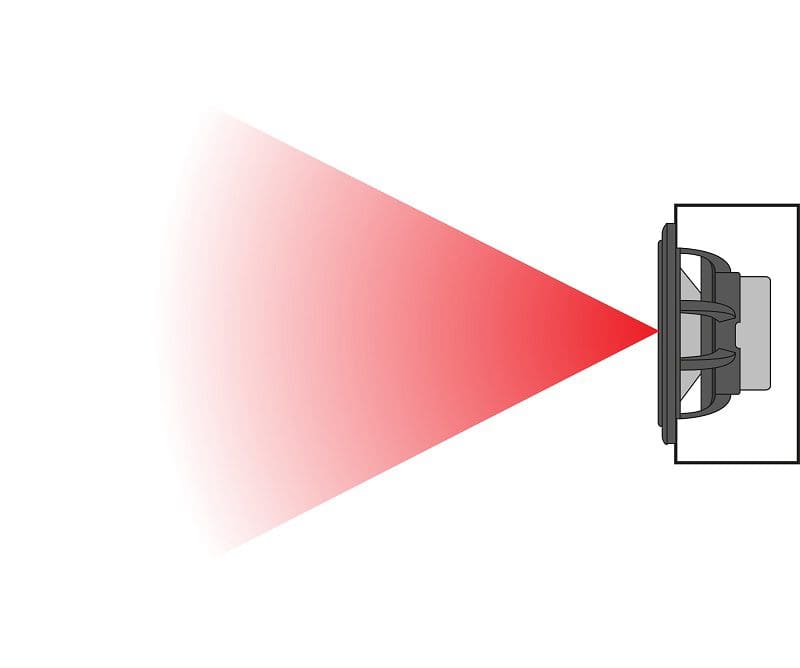
The last topic we’ll mention is directivity. Every speaker, from every brand and of every size, is subject to a phenomenon called directivity. In short, directivity describes how directional the sound of a speaker is. At relatively low frequencies, the sound created by a speaker radiates in a sphere from the cone.
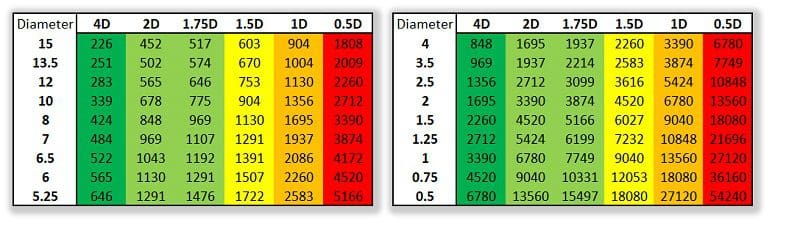
As frequency increases, all speakers become more directional. The frequency at which this starts to happen depends on the diameter of the speaker cone. The chart below indicates (in green) maximum frequencies that radiate evenly in all directions. Frequencies in the red zone are only audible directly in front of the speaker.
Knowing about directivity, it’s important to choose speakers that will sound good in your vehicle’s available locations. For example, a component speaker set with an 8-inch woofer and a tweeter that only plays down to 4 kHz may not deliver good audio performance between 3 and 4 kHz if the listening position isn’t directly on-axis with the speaker. If you can add a midrange driver to the system, you may be better off choosing a 6.5-inch set.
Car Audio Speaker Installation Is Crucial
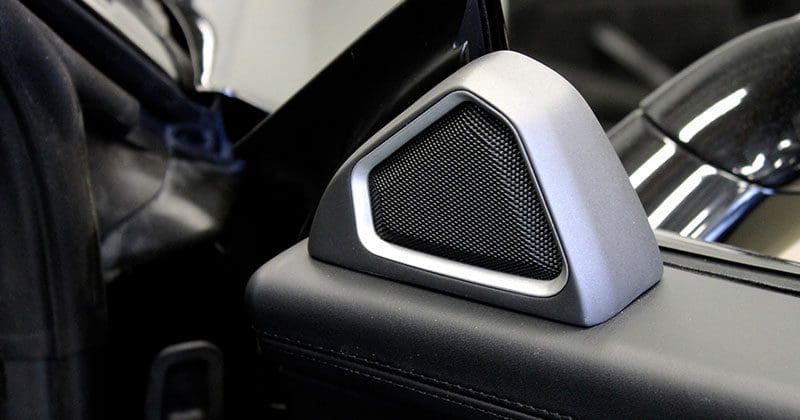
As you can see from the above, working with an experienced specialty retailer is vital to your car stereo system’s performance. Unlike buying home stereo speakers, where the crossovers and enclosures are designed in a controlled environment, car audio installation experts have to use their knowledge and training to create a speaker system from scratch. The tools and training they offer can be the difference between music that sounds realistic and an audio system plagued by distortion and poor frequency response. Lead-In Image Credit: Musicar Northwest in Portland designed these enclosures to house a set of Morel tweeters in the doors of this 2009 Ferrari F30 Spyder. This article is written and produced by the team at www.BestCarAudio.com. Reproduction or use of any kind is prohibited without the express written permission of 1sixty8 media.